Food and mood [re-release]
February 2026. Listen here: And available everywhere you listen to podcasts: https://pod.link/thehealthyhandful About this episode Just like the rest of…

Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) medications, like Ozempic and Wegovy, have transformed the way diabetes and weight are managed. First developed to regulate blood sugar levels, they’re now widely recognised for their role in supporting appetite control and weight loss.
But what foods are best for people using GLP-1s? Which nutrients require special attention? And where do nuts fit in?
Did you know? GLP-1 is just one of the hormones involved in appetite regulation. Others include glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), ghrelin, peptide YY (PYY) and pancreatic polypeptide (PP) (1).
GLP-1 is a hormone released by the small intestine after eating, in response to carbohydrate and fat.
It stimulates the pancreas to release insulin, which helps move glucose from the bloodstream into the body’s cells, providing them with energy. In doing so, GLP-1 helps regulate blood sugar levels.
It also slows digestion (stomach emptying), which helps control appetite.
Did you know? Evidence suggests that nut consumption leads to improvements in insulin sensitivity, a marker of metabolic health and a favourable metabolic environment, important for weight maintenance over the long-term (2).
GLP-1 medications, also called GLP-1 agonists, mimic the effects of the body’s natural GLP-1 hormone. They help reduce food cravings, increase feelings of fullness, slow digestion, and support blood glucose control (3).
Collectively referred to as ‘GLP-1s’, these medications have been used to treat type 2 diabetes for about two decades. More recently, they have gained attention for their effectiveness in promoting weight loss in people with obesity.
In Australia, GLP-1 medications are available only by prescription and are typically administered through self-injection.
Studies have found that people taking GLP-1s for obesity feel significantly less hungry and eat fewer calories – typically around 16-39% less (4).
Using GLP-1s can present several challenges (4), including:
Sustainable weight loss takes more than medication – it also relies on healthy nutrition and lifestyle choices (4,5).
Five key goals include:
Develop eating patterns, made up of a variety of healthy foods, that can be sustained long-term, as this will also benefit physical and mental health, and overall wellbeing (4). Plus, a balanced diet plays a key role in enhancing the effectiveness of GLP-1s.
Nuts naturally help regulate appetite, balance blood glucose levels, and keep you fuller for longer (6).
When food intake drops, due to reduced appetite, nutritional quality becomes more important than ever. Small, frequent meals and snacks can help, as can focussing on nutrient-dense, minimally-processed foods, including fruit, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, lean proteins, nuts, and seeds.
Because nuts are naturally nutrient dense, they provide a concentrated source of plant protein, fibre, healthy fats, micronutrients, and antioxidants. Though small in volume, a handful of nuts delivers a powerful nutrient boost.
The weight loss that comes with GLP-1 use is from both fat and muscle loss. Eating enough healthy sources of protein can help preserve muscle mass during weight loss. But this can be difficult to achieve due to reduced appetite or taste aversions.
Experts (4) suggest plant sources of proteins – such as legumes, whole grains, and nuts – along with dairy, seafood, eggs, and lean poultry be encouraged to support overall health, with red and processed meats eaten in moderation.
Practical, lower volume, nutrient-dense protein foods include nuts, seeds, fish, eggs, Greek yogurt, and cottage cheese (4).
GLP-1 medications can cause digestive side effects. A newly-published paper offers advice to combat issues such as nausea, heartburn, and constipation (3).
For those on GLP-1 medications, dietary fibre is important for preventing constipation – together with adequate hydration. Fibre also helps regulate blood glucose levels and promotes satiety.
Along with other plant-based foods, like legumes, vegetables, fruit, whole grains and seeds, a daily nut habit is a healthy way to boost fibre intake.
A recent study (7) found that people taking GLP-1 medications frequently fall short of recommended daily intakes for several essential nutrients, including fibre, calcium, magnesium, potassium, iron, choline, and vitamins A, C, D, and E.
Adequate nutrient intake is needed to help prevent conditions like malnutrition and sarcopenia. And nutritional status in people taking GLP-1s should be monitored regularly.
Current guidelines recommend that anyone who may benefit from obesity treatment – including people using GLP-1 medications – should have access to comprehensive support for healthy weight management (4).
The Journal of the American Medical Association recently published diet and exercise guidance for people taking GLP-1s (3):
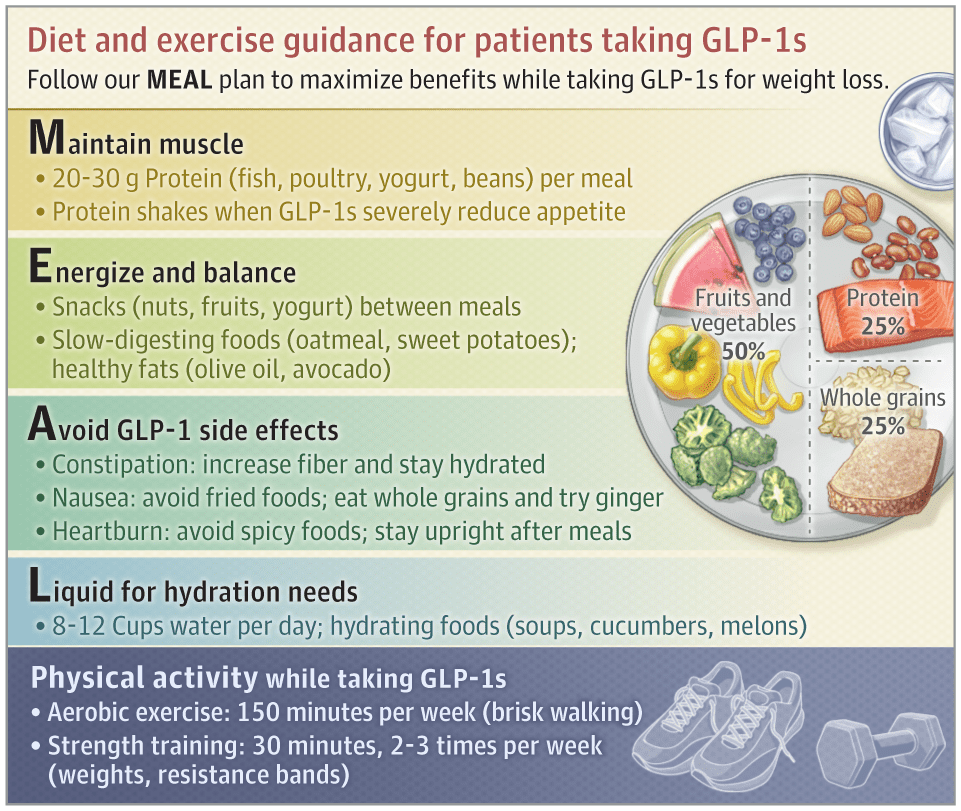
Source: Mehrtash F, Dushay J, Manson JE. I Am Taking a GLP-1 Weight-Loss Medication—What Should I Know? JAMA Intern Med. 2025;185(9):1180.
For GLP-1 users, the aim is quality over quantity – choosing foods that sustain fullness, help regulate blood glucose levels, and provide concentrated nutrition (4).
Adjusting the diet to naturally boost GLP-1 activity shows promise as a strategy to improve health outcomes.
However, evidence is currently limited. More research is needed into the effects of individual nutrients, specific foods, and dietary patterns in humans.
Did you know? A major study, published in 2025, on the link between the intake of various food groups and risk of overweight and obesity found diets rich in whole grains, legumes, nuts, and fruit are linked with a lower risk of overweight and obesity (8).
A major systematic review and meta-analysis on nuts and weight found a ‘high certainty’ of no adverse effect of nuts on body weight (9). Instead, regular, long-term intake of nuts is linked with improved weight outcomes
Did you know? A serve of nuts is 30g, or a handful. But research suggests that up to 120g can be eaten daily, without weight gain (9).
A daily handful of nuts is a valuable addition to the diet of people using GLP-1 medications – helping to increase satiety, regulate blood glucose levels, and provide essential nutrients like fibre, protein, and healthy fats. Their nutrient-density makes nuts an ideal choice for maximising nutrition with smaller portions, and helping to fill nutrient gaps commonly seen in GLP-1 users.
Published November 18, 2025
Be sure to follow us for great recipes,
Nut inspirations and fun facts
For up to date information & the latest research articles